“And then just like that, she was gone from this world, never to be seen or heard from again but forensic medicine has come a long way or has it?”
Cold cases continue to stay at a standstill even to this day, although the number is slowly going downwards, we have come a long way from where we were, in the field of crime and medicine. Investigations, new and old, are cumulative effort to bringing together families torn by grief, additionally giving the answers to the crime thrillers, investigators and doctors when it comes to the dead body. A rest to the soul, is a case that’s solved.
How exactly have we, reached this far, you may ask? It’s all down to DNA phenotypes and genetic genealogy! It’s allowed particular unsolved cases to be reopened with the help of advanced pre-existing technologies. DNA phenotyping is used to track the killer based on physical features that need to be predicted, a gene analysis of unknown individuals. Genealogy allows investigators to compare DNA profiles of profiles to reach a conclusion. It has been primarily known for identifying serial killers by matching to a relative who provided a DNA sample.
Usually combinations of old and new results, that forcefully arise from researching on cold cases are brought forward. A cold case from 1968, had required cranium measurements, skeletal ossification and dental formation timings, radiocarbon estimates, DNA analysis of mitochondrial DNA from a maternal relative all contributed to the quest for answers. These combinations, in many solved cold cases, have also led to the convictions of these murders.
Nivea Vaz
Manipal College of Medical Sciences, Pokhara
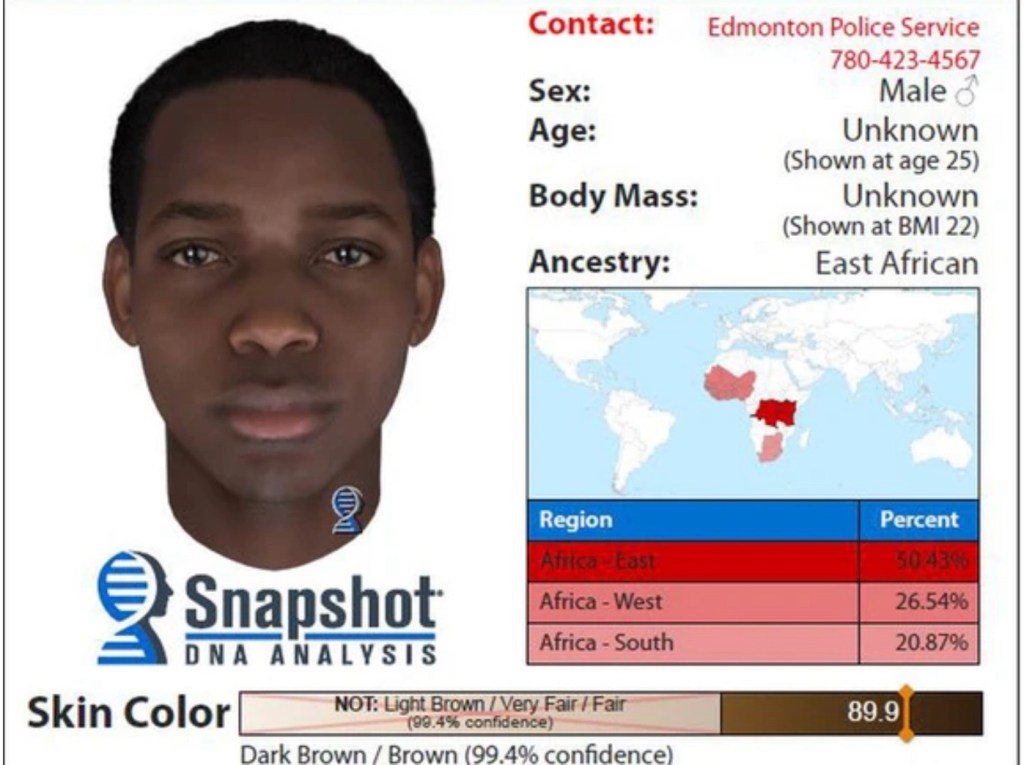
The Edmonton Police Service is, for the first time in its history, using DNA phenotyping in the hopes of identifying a suspect in a 2019 sexual assault. PHOTO BY EDMONTON POLICE SERVICE /SUPPLIED





Leave a comment